pZAP2.1
Shuttle plasmid for the construction of adenovirus vectors with the AdenoZAP2.0 cloning system (in vitro ligation)
- Insertion of heterologous sequences in place of the E1 region of the Ad5 genome ("first-generation" adenovirus vectors)
- E3 region WT or deleted
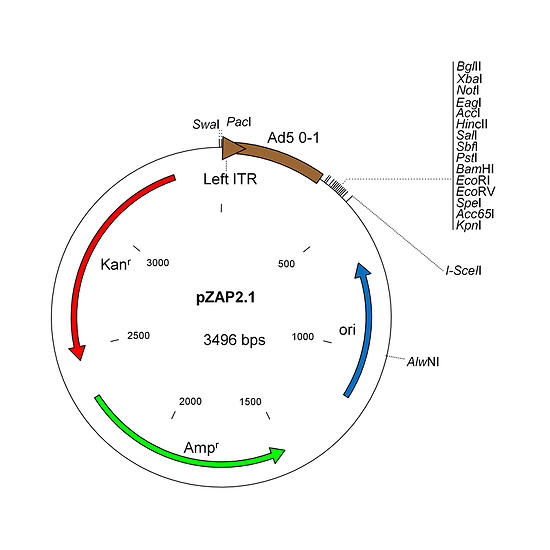
pZAP2.1 is a shuttle plasmid designed for inserting expression cassettes in place of the E1 region of the Ad5 genome, in conjunction with the AdenoZAP2.0 system. It contains a multiple cloning site located downstream from the first map unit (mu) of the Ad5 genome. Expression cassettes should contain promoter-cDNA-polyA signal. The left arm DNA (which includes the left ITR, packaging signal and expression cassette) can be excised from the vector with either PacI or SwaI on one side, and I-SceI on the other side.
| Product | Cat# | Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
pZAP2.2Shuttle plasmid for the construction of adenovirus vectors with the AdenoZAP2.0 cloning system (in vitro ligation or recombination) |
Cat# :
ZP-04 |
20 µg |
$220.00 |
|
RightZAP2.1 DNALinear 32.5 kb Ad5 DNA for the construction of E1-deleted adenovirus vectors with the AdenoZAP2.0 cloning system (in vitro ligation or recombination) |
Cat# :
ZR-03 |
10 reactions |
$450.00 |
|
RightZAP2.2 DNALinear 29.8 kb Ad5 DNA for the construction of E1/E3-deleted adenovirus vectors with the AdenoZAP2.0 cloning system (in vitro ligation or recombination) |
Cat# :
ZR-04 |
10 reactions |
$450.00 |
-
How do I choose the status of the E3 region: wild-type or deleted?
In the adenovirus replication cycle, the expression of the E3 region helps the virus evading the host immune system. This region is not essential for virus replication in vitro and therefore can be deleted in order to construct adenoviruses containing longer transgenes, up to 7.7 kb.
Therefore, if you are using the most common 3.2 kb E1 deletion, and:
- if your expression cassette (= promoter + coding sequence + polyA signal) is smaller than 5.0 kb, you can use adenovirus vectors with either wild-type or deleted E3 region.
- if your expression cassette is larger than 5.0 kb but smaller than 7.7 kb, you must use E1/E3 deleted vectors.
- if your expression cassette is larger than 7.7 kb, you must consider E1/E3/E4-deleted adenovirus vectors.
Notes:
- In some applications such as oncolytic adenovirus vectors (CRAds), it might be desirable to retain the entire E3 region, or increase the expression of some E3 products: for instance, the adenovirus “death protein” E3-11.6K, which facilitates the release of viral particles from infected cells, or gp19K, whose constitutive expression reduces the host cytotoxic T cell response against the vector and increases the persistence of transgene expression on its own but possibly not in the context of constitutive expression of the entire E3 region.
- The E3 region can also be used as a location to insert a second transgene, independent from the one inserted in the E1 region.
-
How do I calculate the maximum cargo capacity of an adenovirus vector?
You simply sum up the sizes of the deletions present in your vector and add 1.8 kb. For instance, let us suppose that you are considering using an Ad5 backbone characterized by a 3.2 kb E1 deletion (psn 354-3510) and a 2.7 kb BglII E3 deletion (psn 28133-30818). Your vector will be able to package 3157 bp (= 3510 - 353) + 2686 bp (= 30818 - 28132) + 1800 bp = 7.6 kb.
The additional 1.8 kb is the extra DNA that Ad5 capsids can package in addition to their 35,935 bp-long genome (Bett et al, J. Virol. 1993; 67: 5911-21).
-
What is the maximum cargo capacity for the AdenoQuick and AdenoZAP system?
For the AdenoQuick1.0 system, the current maximum cargo capacity is achieved with E1/E3/E4-deleted pAd362. The vector allows for inserting 8.9 kb foreign DNA into the E1 region.
For the AdenoQuick2.0 system, adenovirus vectors can be constructed, in which up to 11.2 kb foreign DNA can be inserted. It is done by combining the largest E1 deletion (3157 bp in shuttle plasmid pAd1127-02) with the largest E3 deletion and the hybrid Ad5/35 fiber ( 2686 bp + 756 bp in pAd1129-06), and the largest E4 deletion (2815 bp in shuttle plasmid pAd1130-03), plus the extra 1.8 kb that adenovirus capsids can accomodate in addition to the WT 36 kb genome (Bett et al, 1993. J. Virol. 67: 5911-21).
For the AdenoZAP system, the current maximum cargo capacity of 9.6 kb is obtained with AdenoZAP1.4.
-
What is the difference between the AdenoZAP1.0 and -2.0 systems?
Both the AdenoZAP1.0 and AdenoZAP2.0 cloning systems rely on endonucleases that generate non-symmetrical sticky ends with which directional ligation can be performed. The only difference between both systems is the nature of the enzymes available to excise the left arm from the shuttle plasmid pZAP. In pZAP1.1, the left arm can be excised using PacI or SwaI on the left side, and either SfiI, BstAPI, DraIII, AlwNI or PflMI on the right side. PacI and SfiI are 8-base cutters while BstAPI, DraIII, AlwNI and PflMI are 6-base cutters. In pZAP2.1, the left arm can be excised using PacI or SwaI on the left side and I-SceI on the right side. I-SceI is an intron-encoded endonuclease that recognizes an 18-bp-long sequence within which minimal sequence degeneracy is tolerated.
-
I am using the AdenoZAP system. Which enzyme should I use to linearize my shuttle plasmid before transfecting it into helper cells? PacI or SwaI?
In the AdenoZAP system, you will need to excise from your shuttle plasmid a DNA fragment containing the left ITR, the packaging signal and your expression cassette. Two enzymes are available to cut on the ITR side: PacI and SwaI. Make sure that the enzyme you choose does not cut inside your expression cassette. Since both PacI and SwaI are rare-cutting restriction enzymes that recognize 8 bp-sequences, having both of them in your expression cassette should occur very rarely.
If neither PacI nor SwaI cuts inside your transgene, there is really no preference. Because the PacI site is immediately flanking the start of the adenovirus genome, the DNA ends generated by PacI resemble the most the ends obtained from deproteinised virion DNA and might therefore be more efficient in promoting virus replication. In practice however, no difference in the time needed to recover the virus after DNA transfection into 293 cells is observed between both settings. Virus plaques can appear as early as 4 days after transfecting PacI- or SwaI-digested DNA into 293 cells.
If one of the two enzymes cuts inside your transgene, use the other one.
If both SwaI and PacI cut you transgene, eliminate one of them by site-directed mutagenesis, or use another adenovirus construction method.
-
In the AdenoZAP cloning system, what is the difference between pZAP1.1 and pZAP1.2, and also between pZAP2.1 and pZAP2.2?
pZAP1.1 is the basic AdenoZAP shuttle plasmid. It contains the adenovirus left ITR, packaging signal, and a multiple cloning site. With this plasmid, you can generate recombinant adenovirus vectors only by ligating the "left arm" to the "right arm" and transfecting the ligation products into 293 cells. pZAP1.2 is a derivative of pZAP1.1 wherein a 400 bp-long sequence corresponding to bp 3504-3907 in the Ad5 genome was inserted downstream from the multiple cloning site. With that plasmid, you can generate adenovirus vectors either by ligation and transfection as described above for pZAP1.1, or by transfecting the left arm and the right arm together into 293 cells and have them recombine with each other inside the cell. The same relationship is true between pZAP2.1 and pZAP2.2.
-
Which facilities are required to work with adenovirus vectors?
The National Institute of Health has designated adenovirus as Level 2 biological agent. For most applications, working with adenovirus requires therefore a Biosafety Level 2 (BL2) facility. The NIH guidelines for research involving recombinant DNA molecules stipulate also that experiments which are likely to either enhance the pathogenicity (e.g. insertion of a host oncogene) or to extend the host range (e.g. introduction of novel control elements) of viral vectors under conditions that permit a productive infection should be performed in BL3 facilities.
A BL2 laboratory should contain:
- A warning sign on the entrance door limiting the access to authorized persons only. The sign should identify the agent, list the name and phone number of the lab director or other responsible person, and indicate any special requirement for entering the lab.
- A Class II biological safety cabinet. A Class II cabinet is a ventilated cabinet for personnel and product protection having an open front with inward airflow for personnel protection, and a HEPA filtered mass recirculated air flow for product protection. The face velocity of the inward flow of air through the full-width open front is 75 feet per minute or greater.
- At least one tissue culture incubator dedicated to infected cell cultures. Another separate incubator is desirable for growing uninfected cells.
- The minimal equipment to handle adenovirus culture without exiting the BL2 lab (such as centrifuges, microscope…).
- A sink for hand washing
- A chemical disinfectant kit or at least a gallon of bleach available for spills
For more information about guidelines, visit this NIH web page.
-
Which precautions should I take while working with adenovirus?
Work with adenovirus must be performed in a BL2 lab. There you must:
- Always wear a lab coat while in the virus lab. Before exiting the laboratory for non-laboratory areas (e.g. cafeteria, library, administrative offices…), remove your lab coat and leave it in the laboratory.
- Avoid skin contamination with the virus. Always wear gloves (one pair OK, two pairs better for added protection). Once your gloves have been in contact with infectious material, do not touch common appliances such as telephone or doors handles. Change your gloves frequently.
- Keep the lab doors closed while work is in progress.
- Use mechanical pipetting devices. Do not pipet by mouth.
- Decontaminate all work surfaces after you finish your work, and immediately after any spill. Spray a 10% bleach solution, wipe and spray again a 70% ethanol solution. For large liquid spills, add directly concentrated bleach to the liquid, leave for at least 5 minutes, and wipe.
- Perform all procedures with infectious particles in the biosafety cabinet to minimize the exposure of personnel to aerosols. Minimize the creation of aerosols by pipetting virus cultures and suspension very gently. Use aerosol-resistant tips for pipetting virus suspensions. Do not conduct work with infectious materials in open vessels on the open bench.
- Use needle-locking syringes or disposable syringe-needle units for the injection or aspiration of infectious fluids. Extreme care should be used to avoid auto-inoculation and aerosol generation. Needles should not be bent, sheared, replaced in their sheath or guard or removed from the syringe following use. The needle and syringe should be decontaminated by pipetting in and out concentrated bleach a few times and then promptly placed in a puncture-resistant container.
- Decontaminate all contaminated liquid or solid wastes before disposal. Before starting your virus work, pour some bleach into a beaker. Rinse all materials (tissue culture dishes, pipets, tips…) that came into contact with adenovirus with 10% bleach inside the hood before discarding them in the Biohazard trash and autoclaving. Place all materials to be decontaminated off-site in a durable leakproof container which is closed before removal. If possible, leave the contaminated materials in contact with bleach for a few hours before autoclaving (e.g. after rinsing your pipets with concentrated bleach inside the hood, soak them in a cylinder containing 10% bleach before autoclaving).
- Do not leave the BL2 laboratory with live viruses, unless they are in a sealed tube. Cell cultures transduced with adenoviruses should be inactivated either chemically or biochemically before leaving the BL2 facility.
- Store your adenovirus preparations at –70 °C in closed containers labeled with Biohazard warning signs.
- Wash your hands when exiting the laboratory.
| Vector Map | Polylinker | Sequence | Product Information Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vector Map | pZAP2-1_MCS.png (355.91 KB) | pZap21.txt (4.57 KB) | Product_Information_pZAP21.pdf (46.77 KB) |