AdenoQuick 1.0 Kit
Mono- or dicistronic, replication-deficient or oncolytic adenovirus vectors, max 8.9 kb cargo, 2 cloning steps in E. coli
- Transgene insertion in place of the E1 and/or E3 region
- Ad5 backbone
- E1/E3/E4 deleted adenovirus vectors
- Bipartite (dicistronic) adenovirus vectors containing two expression cassettes, one in the E1 region, and the other in the E3 region
- Oncolytic, conditionally-replicative adenovirus vectors (CRAd's), with or without expression cassette in the E3 region ("armed" or not)
- Kit includes: Adenovirus backbone plasmid, shuttle vector(s), reagents for cosmid construction, adenovirus DNA used as positive control for virus rescue
Make your kit
pAd288 Visit Product Page »
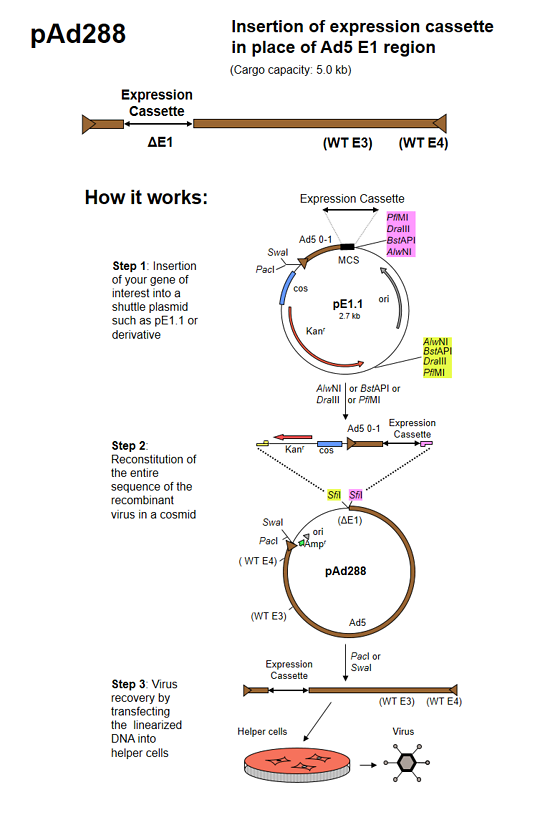
pAd288 (formerly known as AdenoQuick1.1 DNA) is a 39.3 kb plasmid that contains the sequences encompassing bp 3504-right end (9.8–100 mu) of the Ad5 genome. The two SfiI sites naturally present in WT Ad5 DNA were mutated by substituting A for G and C at positions 16291 and 16294 in the Ad5 genome, and C and G for respectively G and C at positions 23001 and 23004 in the Ad5 genome, introducing silent mutations in the adenovirus pVII and DNA-binding protein coding sequences. Two SfiI sites that allow for directional cloning replace the E1 region. The E3 region is intact. The right ITR is flanked by PacI and SwaI sites. pAd288 is used in combination with shuttle plasmid pE1.1 and derivatives to construct replication-deficient adenoviruses containing transgenes in place of the E1 region. The maximum transgene capacity is 5.0 kb.
The entire sequence of pAd288 was confirmed experimentally.
pE1.1 Visit Product Page »
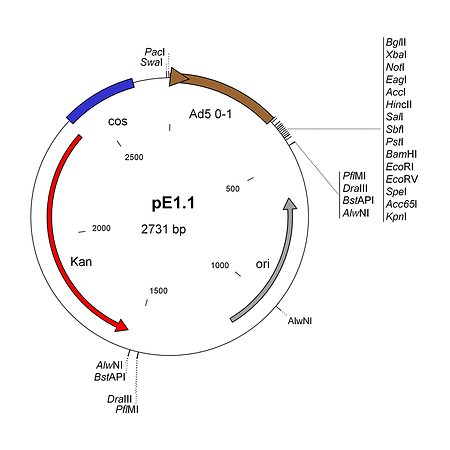
pE1.1 is a shuttle plasmid designed for inserting expression cassettes in place of the E1 region of the Ad5 genome, in combination with the AdenoQuick1.0 plasmids such as pAd288, pAd291, pAd361, pAd362, etc... It contains the first 353 base pairs (map unit 0-1) from the Ad5 genome (including the left ITR and packaging signal), preceded by PacI and SwaI sites, and followed by a multiple cloning site. Expression cassettes inserted into this site should contain a promoter, coding sequence and a polyA signal. The sequences encompassing the kanamycin-resistance gene, the λ cos site, the adenovirus 0-1 map units and the multiple cloning site are flanked by two sets of restriction sites AlwNI, BstAPI, DraIII and PflMI which generate incompatible and non-symmetrical sticky ends. pE1.1 can also be used in combination with vectors pAd329 and pAd330 to construct conditionally replicative adenoviruses (CRAds) containing a heterologous promoter in front of the E1A TATA box.
The AdenoQuick cloning system is designed to construct adenovirus expression vectors that contain one or two expression cassettes in the E1 and E3 regions. It can also be used to construct oncolytic adenoviruses that contain a specific promoter controlling the expression of the E1 region, with or without transgene expression from the E3 region. The method is based on the construction of a large cosmid that contains the entire genome of the recombinant virus and that is transfected into helper cells in order to recover the virus.
Three steps are required:
- Shuttle plasmid construction. The expression cassettes (or any DNA sequence of interest) are cloned into shuttle plasmids that contain bacterial selectable markers.
- Cosmid construction. Using a versatile set of restriction enzymes that allow for directional cloning, the expression cassettes and the selection markers are transferred into large plasmids that contain the adenovirus genome.
- Transfection. The resulting cosmid is linearized and transfected into helper cells in order to rescue the virus.
The AdenoQuick1.0 cloning system includes a series of large plasmids that contain various Ad5 backbones, and their shuttle plasmids. The table below offers a synopsis of the different adenovirus backbones with the status of their E1, E3, and E4 regions, the corresponding shuttle plasmid(s), applications, and maximum cargo capacity.
| Adenovirus Backbone | Features | Shuttle plasmids | Applications | Max Cargo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E3 | E4 | ||||
| pAd288 (aka AdenoQuick1.1) | Δ 3.1 kb | WT | WT | pE1.1 | Expression cassette in place of the E1 region | 5.0 kb |
| pAd291 (aka AdenoQuick1.2) | Δ 3.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | WT | pE1.1 | Expression cassette in place of the E1 region | 7.6 kb |
| pAd292 (aka AdenoQuick13.1) | Δ 3.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | WT | pE1.2 & pE3.1 | Bipartite viruses: expression cassettes in place of the E1 and E3 regions | 7.4 kb |
| pAd361 | Δ 3.1 kb | WT | Δ 1.2 kb | pE1.1 | Expression cassette in place of the E1 region | 6.2 kb |
| pAd362 | Δ 3.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | Δ 1.2 kb | pE1.1 | Expression cassette in place of the E1 region | 8.9 kb |
| pAd363 | Δ 3.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | Δ 1.2 kb | pE1.2 & pE3.1 | Bipartite viruses: expression cassettes in place of the E1 and E3 regions | 8.7 kb |
| pAd329 | Δ 0.1 kb | WT | WT | pE1.1 | Oncolytic Ad with specific promoter driving the expression of the E1 region | 1.9 kb |
| pAd330 | Δ 0.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | WT | pE1.1 | Oncolytic Ad with specific promoter driving the expression of the E1 region | 4.6 kb |
| pAd328 | Δ 0.1 kb | Δ 2.7 kb | WT | pE1.2 & pE3.1 | Armed oncolytic Ad with specific promoter driving the expression of the E1 region and an expression cassette in place of the E3 region | 4.4 kb |
Why should you use the AdenoQuick1.0 cloning system to construct your recombinant adenovirus?
- The cosmid technology that our system uses is particularly well suited for the cloning of the 36 kb-long adenovirus genome. Because phage lambda packages DNAs ranging from 39 to 54 kb, the method selects clones containing full-size genomes.
- No homologous recombination event in E. coli is necessary, thus:
- There is no danger for an unpredicted recombination in E. coli that would not be detected by restriction analysis and would cause the DNA to be non-infectious.
- There is no need for the transformation of a recA+ strain (e.g.. BJ5183) for the recombination and the subsequent transfer to a recA endA strain for plasmid preparation. Phage lambda infection can be performed directly into recA endA strains such a DH5a, XL-1 blue or Top10.
- The cosmid construction is very efficient:
- Expression cassettes are linked to a bacterial positive-selection markers (Kanamycin-resistance gene or lambda cos site). Therefore their presence is ensured in the resulting construct. Please note that the Kanamycin-resistance gene is not inserted into the recombinant Ad genome.
- The restriction sites used for cloning (SfiI, AlwNI, BstAPI, DraIII, PflMI) generate non-symmetrical cohesive ends suitable for directional cloning.
- The cosmid construction via packaging into phage lambda generally produces hundreds of clones, with ~ 100% efficiency. The cosmid construction by electroporation is about 70% efficient.
- One mL bacterial culture can yield up to 3 µg cosmid DNA.
- The method is fast:
- Two expression cassettes can be introduced simultaneously into the viral genome.
- Plaques usually appear 7 to 10 days after transfection, sometimes as early as 4 days.
- The method is versatile:
- Six different enzymes are available to excise the expression cassettes from the shuttle vectors.
- Two rare-cutting enzymes (PacI and SwaI) are available to linearize the cosmid before transfection into helper cells (such as 293...). Therefore, this method is likely to be useful in a very large number of applications.
- The reconstitution of the genome of the recombinant virus in a cosmid can be performed either via packaging into phage lambda or by electroporation.
- Compared to other techniques that also reconstitute the entire sequence of the recombinant virus in plasmid, AdenoQuick requires less “hands-on” time: given the very high percentage of correct clones obtained using the lambda system (~100 %), only a limited number of clones needs to be analyzed at small scale (mini preps). Experienced users can directly set up a midi-prep or maxi-prep in order to obtain transfection-grade DNA.
The AdenoQuick1.0 cloning system is ideal for constructing:
Adenovirus Expression Vectors
- E1-substituted adenovirus vectors, wherein the transgene expression cassette (promoter + coding sequence + polyA signal) is inserted in place of the E1 region. This is the most used adenovirus vector, also called "first-generation".
- E3-substituted adenovirus vectors, wherein the expression cassette of interest is inserted into the E3 region, while the E1 region is kept empty. This type of vector can be used to avoid the emergence of replication-competent adenoviruses (RCA) during virus amplification in 293 cells. Indeed, if the viral vector recombines with the WT E1 region inserted into the 293 cell chromosome, a viral genome will be generated, which will be too long to be packaged, and will not generate viral particles. If necessary the size of the vector is brought to about 36 kb using stuffer DNA
- E1- and E3-substituted bipartite (dicistronic) adenovirus vectors, which contain 2 independent expression cassettes, one in the E1 region and the other in the E3 region. Applications include:
- Vectors containing your gene of interest in the E1 region, and a reporter gene in the E3 region, or vice-versa
- Vectors containing inducible expression systems
- Vectors expressing a regulator and a regulated gene
- Vectors expressing two genes involved in the same pathway
- E1/E3/E4-deleted adenovirus vectors, with expression cassettes in the E1 or the E3 regions, or both (so-called "second generation" adenovirus vectors)
Oncolytic Conditionally-Replicative Adenovirus Vectors (CRAd's)
- Adenovectors wherein a cell-specific promoter drives the expression of E1a, so that the virus replicates only in that cell type (specific tissue, tumor....)
- Additional transgenes ("therapeutic", killer, reporter genes) can be inserted in other regions of the virus such as E3.
- Ad5 backbone
- E1 region:
- 3.1 kb deletion, corresponding to bp 354-3,503 in the Ad5 genome
- 0.1 kb deletion corresponding to bp 354-466 in the Ad5 genome
- E3 region:
- WT
- 2.7 kb BglII deletion, corresponding to bp 28,133-30,818 in the Ad5 genome
- E4 region:
- WT
- 1.2 kb deletion, corresponding to bp 35,319-35,355 in the Ad5 genome and including ORF1-4
AdenoQuick1.0 Manual
The AdenoQuick1.0 manual contains all the instructions to construct adenovirus expression vectors using the AdenoQuick1.0 system, including:
- Shuttle plasmid construction
- Cosmid construction
- Virus Rescue
The manual contains also safety guidelines for handling adenovirus vectors, and detailed plasmid maps.